Asset Packs
Intro
Asset Packs are an exclusive feature of Xtreme Firmware that allows you to load custom Animation and Icon sets without recompiling the firmware or messing with manifest.txt files (as a user). Here you can find info on how to install Asset Packs and also how to make your own.
How to install Asset Packs?
Installing Asset Packs is quite easy and straightforward. First, make sure you're on an updated version of XFW before you begin, Asset Packs were added in v40! Then, find some packs to install (we have a channel in our discord where you can find some) or make your own (see below). Once you have some packs to install:
Open qFlipper and navigate to
SD Cardand intodolphin_custom; if you do not see this folder, try reinstalling the firmware, or create it yourself.Here (
SD/dolphin_custom) is where all Asset Packs are stored. Simply unzip your packs and upload the folders here.If you did this correctly, you should see
SD/dolphin_custom/PackName/Animsand/orSD/dolphin_custom/PackName/Icons.Now simply open the Xtreme Settings app (from the home screen press
Arrow UPand thenXtreme Settings) and select the asset pack you want. When you back out, Flipper will restart and your animations and icons will use the ones from the selected pack!
How do I make an Asset Pack?
Before we begin, it's better to understand a little on how they work. Asset Packs are made of 2 parts: Anims and Icons.
Animations
Animations use the standard and already well documented animation format, so this will be just a quick recap with the key differences mentioned.
The basic animation structure is:
ExampleAnim and AlsoExample are the individual animations, they contain the animation frames compiled as frame_x.bm (this is a special format Flipper uses, it can't understand .png but only raw pixel data which is what .bm is). Each animation has its own meta.txt, which contains information such as image width and height, frame rate, duration and so on. Next to all the animations you have manifest.txt which tells Flipper when and how to show each animation with values like level and butthurt (mood) constraints and weight (random chance weight).
Again, this is all fairly standard Flipper animation stuff, there are plenty of tutorials on YouTube. The key differences with the Asset Pack animation system are:
They go in
SD/dolphin_custom/PackName/Animsinstead ofSD/dolphin.XFW has up to level 30, so make sure to update your manifest.txt accordingly!
Icons
With icons there are quite a few differences and issues we had to solve. In particular, they are usually compiled along with the firmware, so loading them dynamically required a special system. Also, for the same reason, some metadata for the icons now has to be stored along with them, since it's not in the firmware itself. And finally, icons can both be static and animated, both with different solutions to the above problems.
Static icons
The .bm format does not include image width and height, with animations that is stored in meta.txt, so for static icons we made a special format: .bmx, which is [ int32 width ] + [ int32 height ] + [ standard .bm pixel data ], but this is handled by the packer (see below) so don't worry abou it.
Animated icons
Animated icons are structured similarly to animations, but are used like icons. They live next to other static icons, but are stored as .bm sequences. To avoid storing redundant data with .bmx, we kept the frames as .bm and instead opted for a meta file (no extension), which consists of [ int32 width ] + [ int32 height ] + [ int32 frame_rate ] + [ int32 frame_count ], but once again don't fret as this is handled by the packer (see below).
Structure
Other than those few differences above, we kept the same icon naming scheme and structure, so this should look familiar otherwise.
The basic icon structure is:
Which is the same you can find in the firmware source code, in assets/icons. The key differences/things to remember with the Asset Pack icon system are:
Not all icons are supported (see below).
The pixel numbers in the filename are ignored, they are there purely because of the original Flipper icon names and for a hint as to how you should size your icons, but they are not enforced.
We kept the original naming scheme and file structure for compatibility, but the original setup is quite bad, so bear with us. Some icons in subfolders (like
SubGhz/Scanning_123x52) are used in other unrelated apps/places.Some icons in the official firmware have different versions with different numbers to indicate the flipper level they target. Since our system has so many levels, we decided to keep it simple and remove the level progression from icons. For example
Passport/passport_happy1_46x49becomesPassport/passport_happy_46x49andAnimations/Levelup1_128x64becomesAnimations/Levelup_128x64.The
Passport/passport_DBis the background for the passport page, it doesn't mention a pixel size because it should be the same as the Flipper screen size (128x64).
Here are all the icons this system currently supports:
Cool, I read all that, but how do I make one???
All the .bm and .bmx struggles are dealt with by the packer system, which is in scripts/asset_packer.py; when making your Asset Pack you will only be working with .png images and meta.txt/manifest.txt/frame_rate files. As explained above, packs are made of 2 parts, Anims and Icons, but you don't have to include both - if you only include Anims, then the default SFW Icons will be used, and viceversa. You have 2 options: make standalone Asset Packs (recommended), or build them along with the firmware.
Standalone Asset Packs
(First time only) Install Python (3.10 recommended, but not required), then open a terminal/console and run
pip3 install Pillow heatshrink2.Make a NEW folder anywhere on your system where you'll put all your source asset packs. If you're not sure, the Desktop is always a good place, so make the NEW folder there.
Inside the NEW folder make ANOTHER folder with the name of your Asset Pack (less than 32 characters). Inside THAT one, make the Anims and/or Icons folders.
If you used the desktop, you should have
Desktop/AssetPacks/PackName/Animsand/orDesktop/AssetPacks/PackName/Icons.Fill those folders appropriately, referring to the information and structure above, BUT:
Images should ALL be
.png.For animations you add
manifest.txtandmeta.txtfiles.For animated icons you add
frame_ratefiles.Static icons don't need extra configuration.
NOTE THAT THIS IS ALL JUST LIKE IN OFFICIAL FIRMWARE, YOU'RE JUST DOING IT IN ANOTHER FOLDER.
Here is an example of what it should look like:
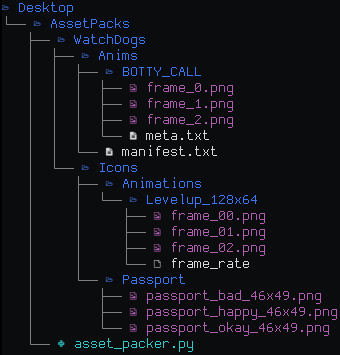
image Copy the
scripts/asset_packer.pyfile into your source packs folder, right next to your asset packs.Run the asset_packer.py script. You might be able to double click it, if not run in console with
python asset_packer.py.It will explain and ask for confirmation, so press Enter.
When it's done (it's usually quite quick) you will have a
dolphin_customfolder right next to your source packs. Inside it you will see your Asset Pack, but in compiled form (.png images swapped for .bm and .bmx).Now upload the packed packs from that folder onto your flipper in
SD/dolphin_custom.Done! Just select it from the Xtreme Settings app now. And if you're generous share your (packed) asset pack in #asset-packs on discord.
Building with Firmware
Follow the steps above, but use
assets/dolphin/customas your source packs folder.Packing is integrated with fbt, so just run
./fbt flash_usb_fullor./fbt updater_packageto compile the firmware, pack the packs and update your Flipper.
Last updated